- Energy is the ability to do work.
- Energy can take many forms, including heat, light, and motion. It can also take the form of electrical, chemical, nuclear, and gravitational energy.
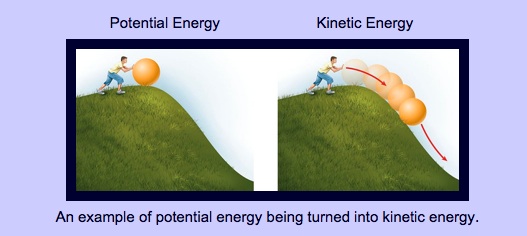
- Energy can be potential (stored) or kinetic (working).
- We use energy for everything we do. Running, cooking, and flying an airplane all require energy.
- An energy source is a source from which energy can be obtained. Most energy sources are also natural resources – naturally occurring materials that are valuable to people and/ or wildlife. Ultimately all energy on Earth is derived from the sun.
- There are renewable and nonrenewable energy sources.
- A renewable energy source is naturally replenished over reasonable geologic time (i.e. tens of years). Some examples include solar energy, wind energy, energy from biomass (plant sources), and hydropower.
- A nonrenewable energy source is a source that cannot be replaced in reasonable geologic time. Fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas are nonrenewable. The Uranium used to produce nuclear power is also classified as a nonrenewable energy source. It would take millions of years to recreate these energy sources.
- Fossil fuels are found deep underground and are generated naturally from decaying plant and animal material exposed to heat and pressure over millions of years.
- Most of the energy used in the United States, the energy used to power homes, fuel our cars, and produce our goods, comes from nonrenewable energy resources. Renewable energy accounts for only about 7% of our total energy supply.
- When fossil fuels are burned for energy, they release harmful substances, including carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and other toxins into the air.
- The carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere from the burning of fossil fuels is a source of global warming. Global warming, the increase in the average temperature of Earth’s air and oceans, is creating global climate change and environmental shifts around the world.
- Excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is also the cause of ocean acidification, the ongoing decrease in the pH level of the world’s oceans.
- 79% of US carbon emissions come from the burning of fossil fuels.
- Sulfur dioxide is also produced by burning fossil fuels. When released into the atmosphere, it causes acid rain and human health problems. Acid rain, or rain with a low pH, negatively impacts terrestrial (land) and aquatic (water) ecosystems.
- We can decrease the environmental problems associated with the burning of fossil fuels by decreasing our energy consumption.
- Scientists are currently developing methods for obtaining energy from clean, renewable energy sources. In the future, we will derive more of our energy from wind, tides, plants, and the sun.
Energy Use in Florida
- Florida’s energy consumption is one of the highest in the country due to frequent air conditioning use.
- On average, each Florida resident burns enough fossil fuel to produce 15 tons of carbon per year on average.
- The state of Florida has plans to produce ethanol, a type of alcohol similar to rubbing alcohol, from citrus as a renewable energy source.
Practice Good Stewardship
- Conserve energy by turning out lights when you are not using them, watching less TV, and taking shorter showers.
- Recycle. It almost always requires less energy to recycle than to create a new product. By using materials more than once, we conserve energy and natural resources.
- Plant a tree. Plants consume carbon dioxide through the process of photosynthesis.. By planting a tree, you’ll help reduce the amount of harmful excess carbon dioxide in our atmosphere.
Review Questions
- What is energy? List at least three forms that energy can take.
- Describe the difference between renewable and nonrenewable energy. Which type of energy is most common in the United States?
- Why are fossil fuels harmful to the environment?
- How can we decrease the environmental problems associated with energy consumption?
Glossary
Acid Rain: Rain with a low pH level caused by pollutants that have been released into the atmosphere.
Energy: The ability to do work.
Energy Source: A source from which energy can be obtained.
Fossil Fuel: Fuel produced over millions of years from the remains of organisms preserved in rocks beneath Earth’s surface over millions of years; includes petroleum, coal, and natural gas.
Global Warming: The increase in the average temperature of Earth’s air and oceans cause by excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Kinetic Energy: Working energy; energy in motion.
Natural Resource: A naturally occurring material that is valuable to people and/or wildlife.
Nonrenewable Energy: Energy derived from a source that we are using up but cannot replace.
Nuclear Power: Energy derived from the splitting of a large nucleus into multiple smaller nuclei.
Ocean Acidification: The ongoing decrease in the pH level of the world’s oceans.
Photosynthesis: The process by which organisms derive energy from the sun.
Potential Energy: Stored energy
Renewable Energy: Energy derived from a source that is naturally replenished over time.